A Comprehensive Guide for Understanding Directory in Python Programming
Mastering Directory Operation in Python Programming
Table of contents
This in-depth article covers everything you need to know about directory management (create, list, rename, remove etc.), including examples on how it's commonly used in large software applications and the built-in module methods Python uses to manage directories. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced Python developer, this article is a must-read to improve your Python skills today!.
Directory
Directory is a location (reserved space in the filesystem) with a unique name to group or collect files or sub directories (directory inside the directory) together. Sometimes in the course of application development there will be need to create a directory to keep files or subfolders on the storage device of the desired operating system (server or user based ) to enable effective and efficient performance. The directory that has collection of subdirectories and files is referred to as root directory.
Handling Directory in Python
Python provides several functionalities to deal with directory (collection of files and subdirectories) in applications. Python uses the os module functions to manage directories.
NB: Except stated to have a different meaning, directory in some context is referred to as folder.
Making a directory in Python
The mkdir of the os built-in module is used to create a directory. For the context of this tutorial let's create a directory (folder) named technical.
NB: When using modules it is best to import them from the beginning of the file.
import os
os.mkdir("technical")
The technical will be created in the root of the current directory where the code is executed from but you can Indicate the path to the location where the folder will be created as an argument in the mkdir method.
import os
os.mkdir("C://......./technical")
Making directory with subdirectories in Python
The makedirs() method from the os module is used to create a directory with subdirectories (directories within it). The code below basically creates a directory name technical and then goes further to create first-month
import os
os.makedirs("technical/first-month")
Get the current directory path in Python
The getcwd() function is used to get the path of the current working directory.
import os
print(f'This is the path of the current working directory: {os.getcwd()}')
# This is the path of the current working directory: C:\....\Python
Reading directory contents in Python
The listdir() function is used to list the files and subdirectories in the current working directory or the path to the directory passed as the argument.
import os
# the getcwd() is used to get the current working directory
current_dir = os.getcwd()
# the listdir() is used to get the current working directory
directories = os.listdir(current_dir)
print(f'Found {len(directories)} directories in {current_dir}')
print('Next Line')
for directory in directories:
print(directory)
Change directory in Python
The chdir() is used to change the directory.
import os
os.chdir('c:/Users/Desktop/')
print(f'Outcome after change of directory: {os.getcwd()} ')
# Outcome after change of directory: c:\Users\Desktop
Rename directory in Python
The rename() from the os module is used to rename directory it takes in two arguments (the first is the old file name and the second the new file name).
In the code below we utilize a couple of os module functions to demonstrate the rename function.
import os
os.mkdir("python-dev")
current_dir = os.getcwd()
os.listdir(current_dir)
os.rename('python-dev','python-codes')
directories = os.listdir(current_dir)
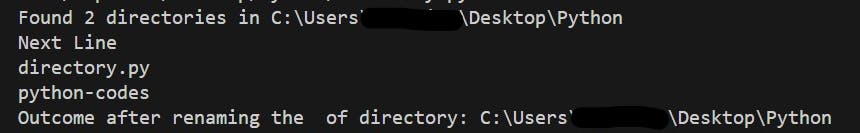
print(f'Found {len(directories)} directories in {current_dir}')
print('Next Line')
for directory in directories:
print(directory)
print(f'Outcome after renaming the of directory: {os.getcwd()} ')
- Outcome
Removing files or directories in Python
The rmdir() function in the os module is used to delete a directory.
The rmdir() returns an OSError exception type if the directory to be removed is not empty.
#OSError: [WinError 145] The directory is not empty: 'python-dev'\
It works fine, If there are no files or subdirectories in the directory to be removed.
import os
os.rmdir("python-codes")
current_dir = os.getcwd()
directories = os.listdir(current_dir)
print(f'Found {len(directories)} directories in {current_dir}')
print('Next Line')
for directory in directories:
print(directory)
print(f'Outcome after deleting the python-codes directory: {os.getcwd()} ')
In order to be able to remove a directory with subdirectory or files the rmtree() function of the shutil module can be used.
import os
import shutil
shutil.rmtree("python-dev")
current_dir = os.getcwd()
directories = os.listdir(current_dir)
print(f'Found {len(directories)} directories in {current_dir}')
print('Next Line')
for directory in directories:
print(directory)
print(f'Outcome after force deleting the python-dev directory: {os.getcwd()} ')
- Outcome

Familiarity with the directory management in Python comes with practical application.
Conclusion
Python programming os module methods provide the ability to create, rename, move, and remove directories or subdirectories on the OS filesystem. However, it's important to exercise caution when granting users the ability to delete or remove a directory and its contents. Confirmation messages can help prevent accidental data loss. Effective directory management is crucial when developing large applications.
Find this helpful or resourceful? kindly share with others and feel free to use the comment section for questions, answers, and contributions.
