Introduction to Polygon for Ethereum scaling and infrastructure development in web3
A simple Polygon walkthrough article for web3 and blockchain developers and enthusiasts
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
In this article, we'll be looking at the Polygon technology which is committed to fostering the growth of Web3 applications by providing the infrastructure needed for Web3.
If you're looking at finding a piece of tailored information to onboarding you on Polygon and its application in web3 then this is the right place for you, because the first time I searched for Introduction to Polygon on the number one most used search engine in the world Google
And about the first 10 results were all talking about Polygon structure and no specific article was available on Polygon technology for this search query.
Moreso when I type " Introduction to polygon web3" it was bringing up the links to different blogs and news about Polygon.
That being said without further redo let's begin:
What is web3?
simply put "The next phase of the internet". Which is intended to bring about decentralization where no organization or team or individual has control over the internet. Web3 is a decentralized digital space based on blockchain technology.
Gavin Wood, the founder of blockchain infrastructure company Parity Technologies, one of the co-founders of the Ethereum cryptocurrency coined the term “Web 3.0” in 2014, laying out his vision of the future of the internet.
Web3 is the internet that is powered by blockchain (the shared ledger systems used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether) and artificial intelligence. Web3 applications run on blockchains, decentralized networks etc. Dapps ( decentralized application is the common term often used for web3 applications.
Packy McCormick, an investor who helped popularize web3, has defined it as “the internet owned by the builders and users, orchestrated with tokens.”
The blockchain is beginning to reach certain capacity limits as a result the number of individuals using Ethereum keeps rising. As a result, the cost of accessing the network has increased, necessitating the use of "scaling solutions." which is one of the solutions provided by Polygon.
What is Polygon?
Polygon is formerly known as the Matic network created in India in 2017 by crypto developers Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun, as well as Mihailo Bjelic. The Matic network attracted some top names in the decentralized finance (DeFi such as Decentraland and MakerDAO after going live in 2020. It was rebranded to polygon in February 2021. After the rebranding, Polygon retained its MATIC cryptocurrency, the digital coin underpinning the network. MATIC is used as the unit of payment and settlement between participants who interact within the network.
Polygon Technology and the development is coordinated by Polygon foundation ( an Indian non-profit). In February 2022 Polygon raised $450 million to scale Ethereum scaling solutions across the globe.
Polygon's purpose is to produce the best scaling solution for Ethereum and the most popular scaling solution is the matric network which is now referred to as the Polygon PoS chain.
Polygon is a decentralised Ethereum scaling platform that enables developers to build scalable user-friendly dApps with low transaction fees without ever sacrificing security. Polygon believes in Web3 for all.
Polygon is the leading platform for Ethereum scaling and infrastructure development. Its growing suite of products offers developers easy access to all major scaling and infrastructure solutions: L2 solutions (ZK Rollups and Optimistic Rollups), sidechains, hybrid solutions, stand-alone and enterprise chains, data availability solutions, and more. Polygon’s scaling solutions have seen widespread adoption with 7000+ applications hosted, 1B+ total transactions processed, ~100M+ unique user addresses, and $5B+ in assets secured. source
Polygon is built to work with a variety of scaling solutions, including both Layer 2 and sidechains. Stand-alone chains and secured chains are the two types of chains enabled by the protocol. The former does not need to rely on Ethereum for security because they use their own consensus processes. Setting up a reliable consensus process, on the other hand, is not an easy task and will undoubtedly be a tall order for many projects. Running a secured chain might be a preferable solution for those.
Polygon's "Security-as-a-Service" concept, which is delivered either directly by Ethereum or by a specialized pool of validators, is used to secure chains.
Benefits of Polygon
Compatible with Ethereum
Speed
Flexibility
Scalable
Easy integration
Polygon Architecture
The Polygon software development kit (SDK) is at the heart of the network, and it's used to create Ethereum-compatible decentralized apps as sidechains and connect them to its main blockchain.
Secured Chains with the Polygon Bridge System
In any scaling solution, a bridge is an essential component.
One of the following construction scalability strategies can be used to build sidechains:
- Plasma Chains
Bundles transactions into blocks and submits them all at once to the Ethereum network.
A plasma chain is a separate blockchain that is linked to Ethereum's main chain and incorporates fraud proofs (such as optimistic rollups) to settle disputes. Because they are effectively smaller replicas of the Ethereum Mainnet, these chains are also referred to as "child" chains.
- Zero-Knowledge (zk) -Rollups
Allows multiple transfers to be bundled into a single transaction. Hundreds of transfers are bundled (or "rolled-up") off-chain and a cryptographic proof are generated. These proofs can be in the form of SNARKs (succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge) or STARKs (scalable transparent argument of knowledge). Validity proofs, such as SNARKs and STARKs, are posted to layer 1. Zero-Knowledge Rollups
- Optimistic Rollups
Like Plasma Chains, but with the added capacity to scale Ethereum smart contracts. ORs (Optimistic Rollups) are a sort of layer 2 architecture that runs on top of Ethereum's base layer rather than on it. This allows smart contracts to be run at scale while still being protected by Ethereum. These structures are similar to Plasma, except instead of running Plasma, they run an EVM(Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatible Virtual Machine called OVM (Optimistic Virtual Machine), which allows ORs to execute whatever Ethereum can. Optimistic Rollups
- Validum Chains
Validity proofs such as ZK-rollups are used, however, data is not saved on the Ethereum main layer 1 chain. This can result in tens of thousands of transactions per second per validium chain, with numerous chains running in simultaneously. Explore Validum Chains Validum - Secured chains with Validum
- Polygon's main chain
is a Proof of Stake (PoS) sidechain where users stake MATIC tokens to validate transactions and vote on network upgrades.
Proof of stake is similar to the way we use the conventional receipt as proof of payment but in the context of web3, it's used to verify new transactions, add them to the blockchain and create new tokens.
Proof-of-stake is a consensus mechanism for cryptocurrencies that allows for the processing of transactions and the creation of new blocks on a blockchain. A consensus mechanism is a way of validating entries in a distributed database while also keeping it secure. In the case of bitcoin, the database is known as a blockchain, and the blockchain is secured by the consensus mechanism.
The Ethereum developers knew from the start that proof of work ( would have scalability issues that would need to be addressed — and, indeed, as Ethereum-powered decentralized finance (or DeFi) protocols have grown in popularity, the blockchain has struggled to keep up, causing fees to skyrocket. For more information about Proof of work or proof of stake and here
- Stand-alone chains
There are fewer standalone chains than secured chains.
Matic is implemented as a blockchain, with its own set of validators and the ability to link to Ethereum using bridges. Matic becomes an Ethereum side chain in this situation.
Polygon can be used to create separate blockchains with control over sovereignty, scalability, and flexibility. That means you could establish a blockchain only for the purpose of managing a company's digital assets, utilizing Polygon's protocol secretly. This is in contrast to public blockchains like Ethereum, which place a premium on security, interoperability, and developer experience.
Polygon architecture consists of four abstract and composable layers.
- Ethereum Layers
The Ethereum layer is the initial layer that is not mandatory (optional) since polygon-based chains aren't required to use it.
Polygon chains can use this layer to gain access to all of the features of the world's leading dApp development platform, including its strong security and programmability. The layer is made up of smart contracts that handle functions like finality, staking, message relaying, and dispute resolution.
- Security Layers
This layer is optional and is in charge of administering the pool of validators used by Polygon's Security-as-a-Service solutions. The layer can be constructed as a meta-blockchain running alongside Ethereum periodically. It can also be implemented directly on Ethereum, with Ethereum miners acting as validators.
Validators check the authenticity of any Polygon chain on a regular basis and are compensated for their work. Validator administration tasks such as registration/deregistration, shuffling, and reward distribution are also handled by this layer.
- Polygon Networks Layer
In Polygon's architecture, this is the first mandatory layer. This layer is made up of a collection of sovereign blockchain networks, each of which serves a specific community. Transaction collation, local consensus, and block production are all functions that each network may handle. The Polygon protocol can also be used to connect the networks and exchange arbitrary messages.
- Execution Layer
The execution layer is the second mandatory layer of the Polygon network that is in charge of interpreting and executing transactions that have been agreed upon and included in the blockchains of the Polygon network. The layer is divided into two parts: the execution environment and the execution logic.
One of the amazing parts of Polygon technology is the blogging feature on the platform where different concepts and solution integrations are published regularly.
Members Assemble
The Polygon Community is a hub for all Web3 enthusiasts. Developers, validators, token holders, creators, builders and believers alike- everyone is welcome aboard!
Polygon solves for high gas fees and slow speeds, without sacrificing security. Also, if you’re building on Ethereum, you're already got all it takes to be a Polygon Developer.

Welcome to the most exciting and innovative platform to build your blockchain application on Polygon Blockchain. Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionise the way the digital world handles data and does business. Be a part of this revolution and get a head start with decentralised application development on Polygon.
This page will act as your guide into the Polygon Ecosystem.
Polygon's documentation is categorised based on the platform and development approach

Polygon Scaling Solutions
- Polygon PoS Live
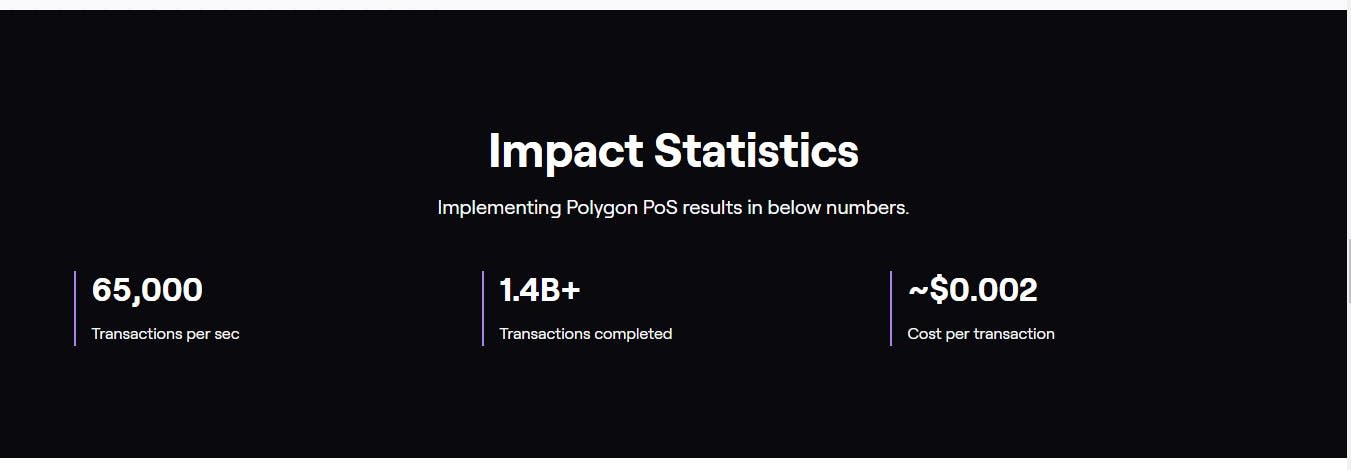
With over 1.3 billion transactions recorded, 130 million unique wallets and ~2.7 million monthly active users, Polygon Proof of Stake (POS) is the most proven scaling solution in web3, and the best way to launch a web3 project that's ready for a global audience. It is an EVM enabled sidechain.
Polygon PoS is a layer 2 scaling solution that achieves unprecedented transaction speed and cost savings by utilizing side-chains for transaction processing. At the same time, POS ensures asset security using the robust Plasma bridging framework and a decentralized network of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) validators.
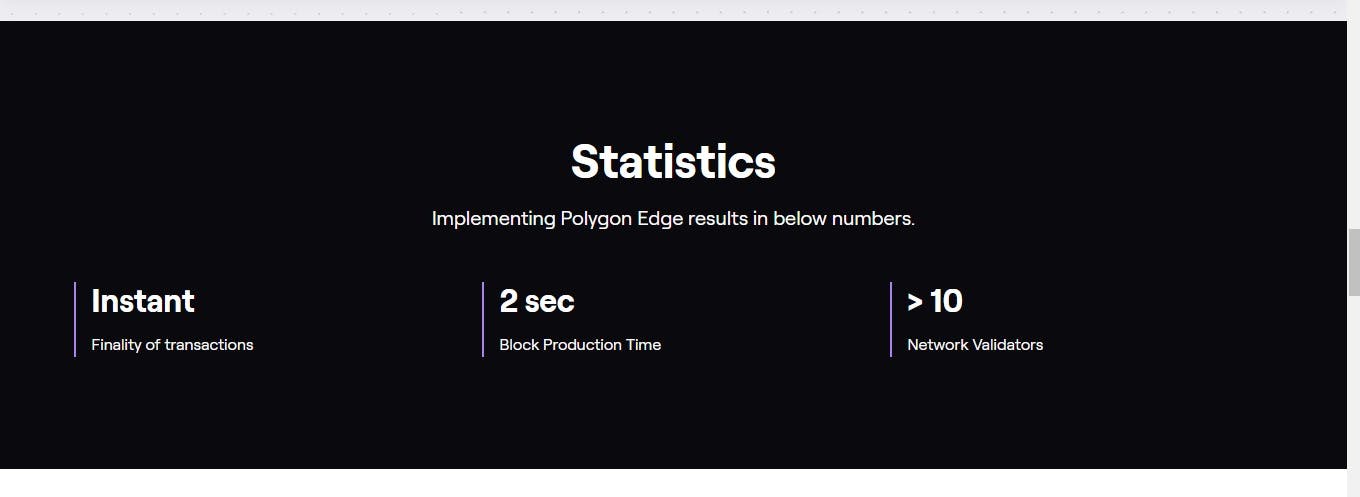
- Polygon Edge Live
A modular and extensible framework for building private or public Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Deploy your own blockchain networks with ease.
Polygon Edge allows you to run your own blockchain network with a variety of features that you can customize. It is guided by the principles of modular architecture and enables Ethereum compatibility with your network.
Polygon Edge modules cover the whole blockchain stack and are designed with developer experience and extensibility in mind.
- Polygon Avail Development
A scalable, data availability blockchain.
A core component of the modular blockchain movement coming in the near future. Targeted towards off-chain scaling solutions and standalone chains.
Avail aims to facilitate a complete change in how we approach the design of blockchain systems. Avail enables modular chain design where various execution environments can use Avail for data ordering and availability. Avail is agnostic to the execution layer, which can be the standalone chains or off-chain scaling solutions that use Avail. The applications hosted on these execution layers enjoy the full security of Avail.

- Polygon Zero Development
Polygon Zero uses the speed of Plonky2 to enable a more scalable and decentralized ZK L2. It offers both rollup and validium modes, giving users access to higher throughput and lower fees. t's very fast with high proof and less secure than miden.
Polygon Zero is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. What separates Polygon Zero from other ZK scaling solutions is the power of Plonky2, our groundbreaking prover system, which generates ZK proofs faster than any other existing tech. Plonky2 supports efficient recursive proof generation, allowing Polygon Zero to scale horizontally, meaning the throughput of the protocol is limited not by the weakest nodes on the network, but only by the total compute available.

- Polygon Miden Development
Polygon Miden is a STARK-based, Zero-Knowledge rollup with support for arbitrary smart contracts
Polygon Miden is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. Miden relies on zero-knowledge technology (zk-STARKs) to “roll-up” thousands of layer 2 transactions into a single Ethereum transaction, thus, increasing throughput and reducing transaction fees. At the heart of Polygon Miden is Miden VM: a Turing-complete STARK-based virtual machine which provides a level of safety and supports advanced features currently not available on Ethereum.

- Polygon Hermez Live
An open-source zk rollup optimised for secure, low-cost and usable token transfers built on Ethereum.
Hermez zk-rollup is a layer 2 construction on top of Ethereum that solves its scalability through mass transfer processing rolled into a single transaction. The "zero-knowledge proof" (ZK) technology is used to present and publicly record the validity and correctness of the rolled transfers processed on the Ethereum blockchain. By storing just the proof and the compressed data of a batch of transfers, the efficiency and the throughput of the network are multiplied.

- Polygon Nightfall Testnet
A privacy-focused rollup for enterprise coming soon. One-of-a-kind privacy-focused rollup that effectively combines the concepts of Optimistic Rollups with Zero-Knowledge (zk) cryptography thus creating a private and scalable transactions solution
Nightfall 3 is an upgraded version of Nightfall aimed to lower the transaction cost of ERC20, ERC721 and ERC1155 token private transfers. It uses Optimistic Rollup for lowering the costs and the privacy is attained by leveraging zero-knowledge proofs. The optimistic rollup contracts are deployed on Ethereum (layer 1). Validators will roll up transactions into blocks and submit them to the Optimistic contracts. Challengers will submit fraud proofs for any invalid block to the same contracts. All the information required to perform a private transfer exists with clients and does not rely on any off-chain third party.

- Polygon ID NEW In the future, our identity will be in digital identity (blockchain native identity).
Polygon ID a self-sovereign private identity solution
Polygon ID is a blockchain-native identity system with programmable privacy that empowers people and enables the creation of trusted interactions with web3 services.
A new class of technological solutions for a censorship-resistant digital identity. Prove access rights and reputation on-chain while keeping user privacy, boost dApps, and DeFi. Open to existing standards and ecosystem development.

Polygon supernets are powered by Polygon edge
Polygon Supernets are the fast-track for blockchain adoption in new private and public networks for dApps and enterprises alike. Polygon Supernets uses powerful Polygon Edge as the configurable infrastructure solution in a highly secure and decentralized environment.

Welcome to the home of all NFT, Gaming, and Metaverse projects that are on the Polygon protocol. We partner with large scale NFT projects for globally recognized IP and Brands, and are the best in class solution for energy efficiency and scaling on the blockchain.
IndiGG is a Sub-DAO of Yield Guild Games (YGG) being built in association with Polygon to create a Play-to-Earn gaming hub within India. IndiGG is building a platform where gamers will discover the future of gaming and embark on a journey into virtual worlds to create economic opportunities for all participants. INDIGG helps games earn real money while ding what they love - play games like Axie Infinity, Pegaxy, Nyan Heroes and more.
It is the first Indian play-to-earn guild powered by YGG and Polygon, to empower and grow the gaming ecosystem in the Indian subcontinent.
As a gaming guild, IndiGG pools funds to purchase yield-generating NFTs, and supports players to invest time and effort to optimize community-owned assets for maximum utility and return.
By merging NFTs and decentralized finance (DeFi), IndiGG creates value for its partners and community by developing the content and economy of virtual worlds and blockchain-based games. The organization’s mission is to create the biggest virtual world economy.
Polygon dApps
The Web3 applications built on Polygon offer low fees, and high scalability, and hold themselves to the highest standard of security.
The following are Polygon dApps
The following Hermez dApps
This is a free online school dedicated to onboarding developers into the world of building Decentralized Applications for the future of the Web. We are here to help you level up your skills every step of the way.
There are 4 levels that a student can achieve through completing this learning journey. For each level, you will need to complete a set of tasks.
Once you successfully set up your environment, you’ll need to review core concepts and complete a mid-term quiz to achieve level 2.
Then, you can begin learning each of our tutorials split into 2 modules; beginners and advanced. Once you complete a module, tweet your GitHub link of an example dapp of your choice to the @0xpolygondevs Twitter account to receive a shout-out and complimentary, limited edition NFT badge!
Conclusion
With the implementation of web3 applications (dApps), their usage in solving problems, and complexity in operations, Polygon intends to make it very simple for all including the cost of transaction fee. This is a tailored article that shows how to explore the Polygon for Ethereum scaling and infrastructure development in web3 in order to know which area to get involved in at ease without going through a lot of details on the internet.
Research Credits and Resources for further reading
What is Web3? The Decentralized Internet of the Future Explained
What Is Web3 and How Will it Work?
Polygon Blockchain Project Explained: A Detailed Look into the leading scaling platform for Ethereum
An In-Depth Guide to Polygon MATIC
Thank you for reading this article.
Please kindly share with your network and feel free to use the comment section for questions, answers, and contributions.